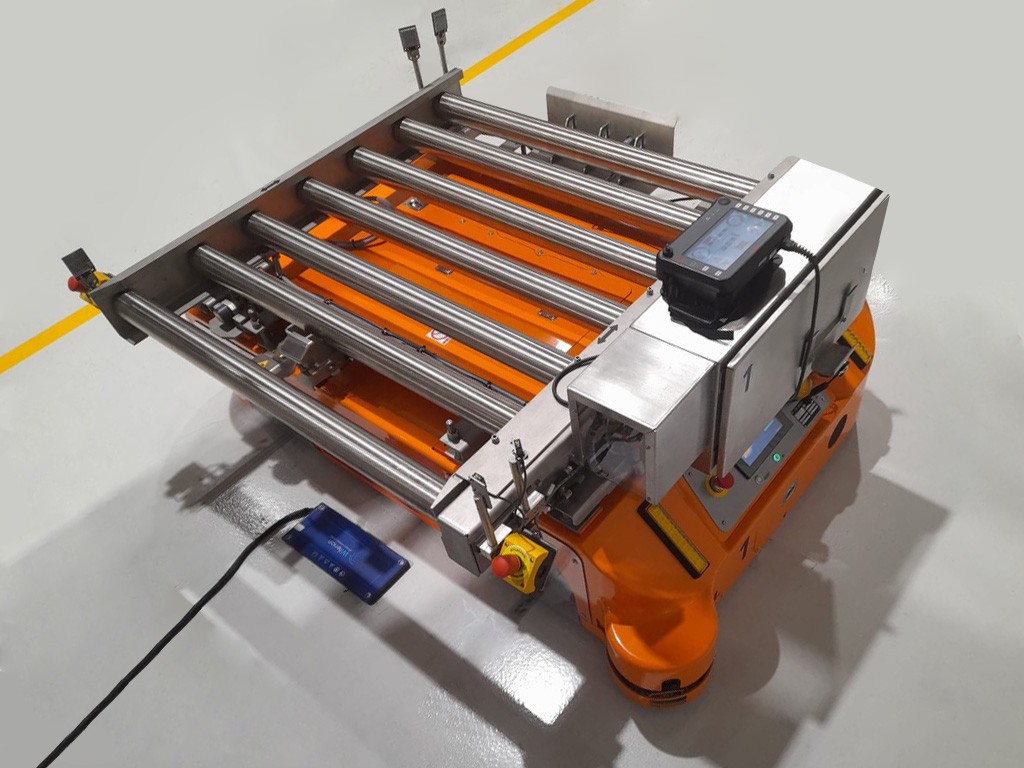
MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW is one of the "most-…" from the whole family MOBOTs
The strongest - can carry up to 1800 kg,
The most powerful - with 4 kW drives,
and now also with the MOST battery charging capability.
MOBOT® with lead acid or lithium batteries?
Everyone can choose for themselves. But what about battery charging? Customers' needs for how to charge a battery in an industrial truck are as varied as their application. For both the first and the second type of battery, it is possible to charge the MOBOT®:
directly via a connector available on the truck to which the operator connects the loader,
through a contact connector mounted under the MOBOT® (e.g. two-way trolleys, trolleys with a hitch) or at the back of the housing (e.g. one-way trolleys), where the truck automatically moves to the contacts of the charger or to them reverses to start charging the battery without operator intervention.
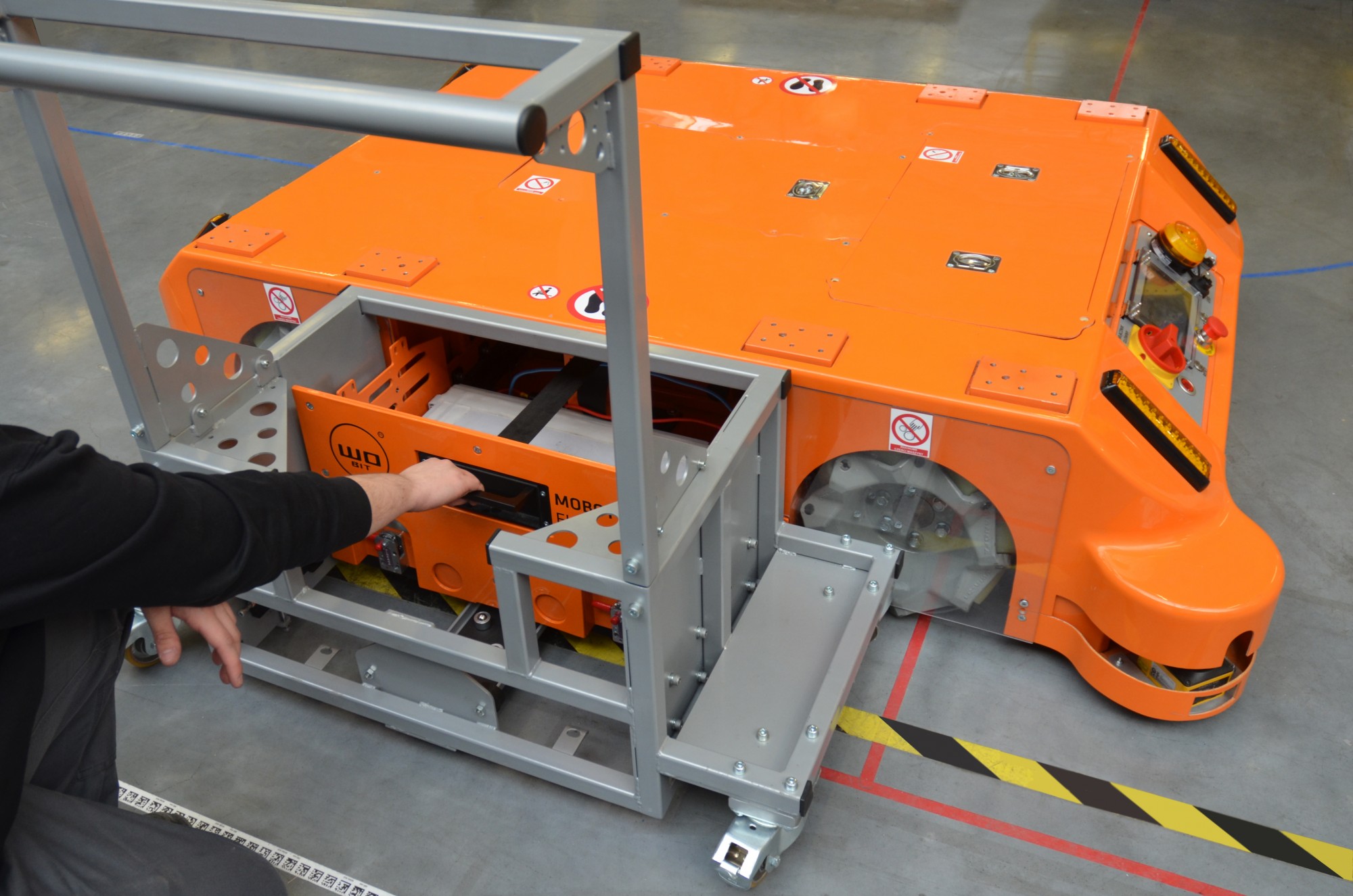
Additionally, MOBOT® lead acid batteries are replaceable. Batteries placed in cassettes can be pulled from the MOBOT® by the operator onto a special trolley and connected to the charger. Thus, the second set of already charged batteries can be placed immediately in the truck.
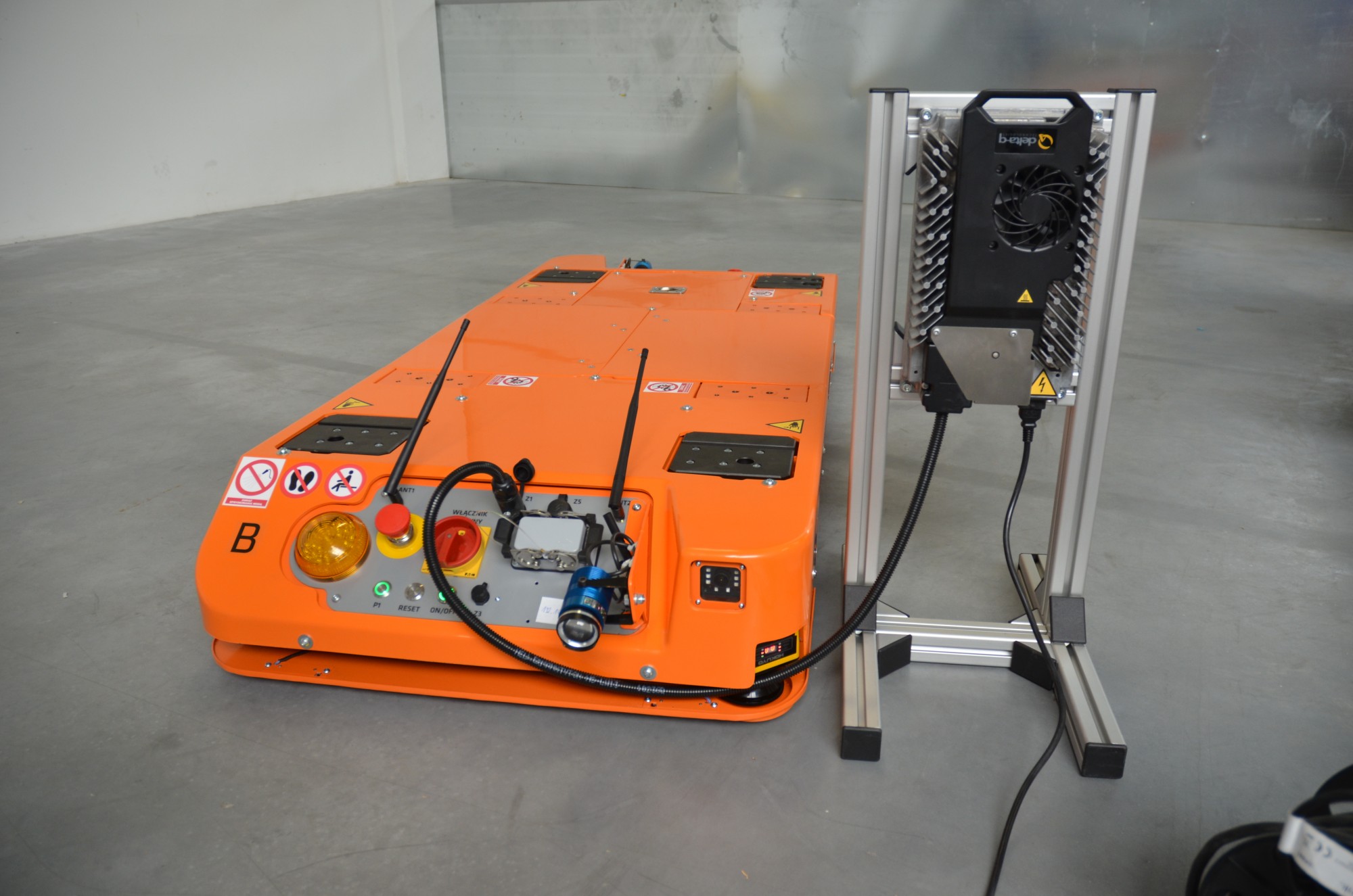
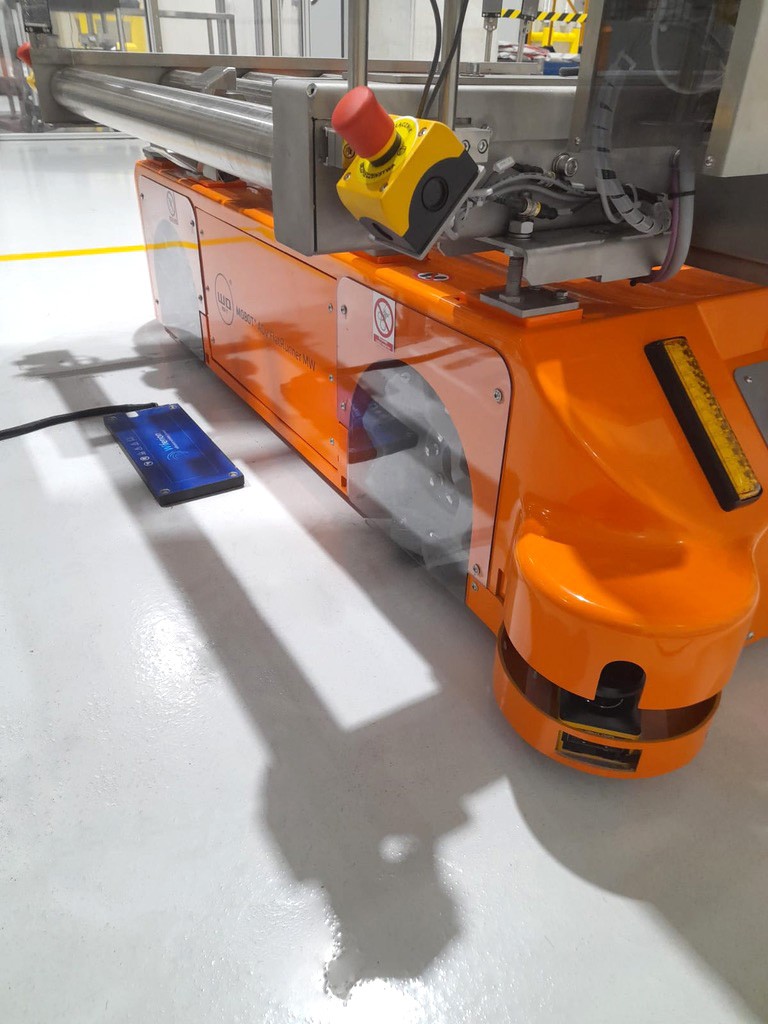
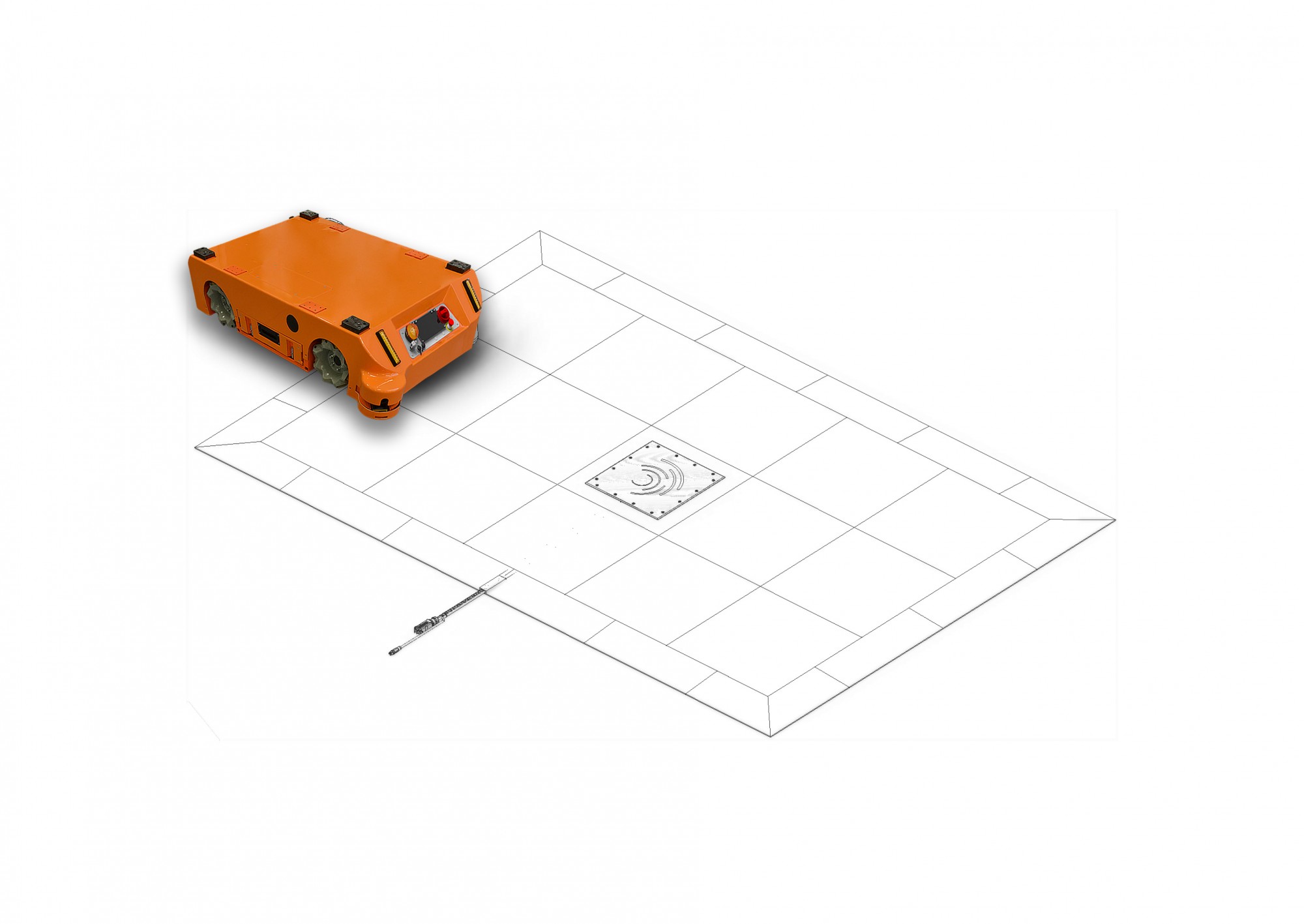
MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW with inductive battery charging system
Recently, thanks to cooperation between WObit and Wiferion, the first industrial trucks MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW are equipped with an inductive charging system for lithium batteries. Positive test results of our engineers from the Research and Development Department, but most of all customer satisfaction, caused that we started design works enabling the use of an inductive battery charging system in a younger and slimmer brother MOBOT®a AGV FlatRunner MW , ie: we FlatRunner MW HT . The use of an inductive charging system for lithium batteries, instead of lead-acid batteries, allowed our MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW to drop as much as 205 kg of its own weight.
No need to connect the charger to the truck manually or replace the battery cassettes by operators improves safety and ergonomics of work. Operators are not distracted by low-battery alerts and action to recharge the battery.
The induction charging system selected by WObit does not require sinking the induction loops in the ground along the entire route of the trolley road car. MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW is equipped with four lithium batteries with a capacity of 21 Ah each and one coil. The second coil and charger are mounted at the charging point. This reduces costs and shortens the time needed to implement a truck with an inductive charging system. MOBOTs equipped with the Wiferion system are easily adaptable to the needs of the solution. In the event of the reorganization of the area where the truck works and its routes, there is no need for additional milling of the floor and sinking of subsequent tapes. In addition, the electromagnetic field is generated only at the points where the truck's batteries are charged, and not for the entire duration of the truck's operation along the entire length of the induction loop. For the Wiferion system, the electromagnetic field is generated during charging at a distance of up to 200 mm to each side from the coil. The PN-EN ISO 3691-4: 2020 standard requires the designation and marking of the charging site as a hazardous area. For MOBOT ®a AGV FlatRunner MW with lithium batteries and inductive charging, this area is kept to a minimum - an area equal to the size of the MOBOT® and the charger itself.
Thanks to the new loading method - MOBOT® has become even more autonomous and safe.
High availability of industrial truck
MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW equipped with four 21 Ah lithium batteries each, can work ~ 1.5 hours with maximum load. The actual working time of the trolley is additionally influenced by the driving speed, the route on which the MOBOT® moves (the need to slow down, accelerate due to bends, intersections or stops caused by violating the security zone of the scanners) and the type of flooring. MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW needs ~ 45 minutes to fully recharge the battery.
The system of inductive charging of the truck's battery without an operator increases its availability. The batteries can be recharged at the MOBOT® stopping points, which are also points of reloading of the transported details or a place of waiting for the next task. Appropriate design of the system at the offer stage allows you to determine how many points the chargers should be placed in order for MOBOT® to perform its work continuously. Contrary to lead-acid batteries, the charging process of lithium batteries in the Wiferion system begins almost immediately after the MOBOT® is correctly driven over the stationary coil. By positioning the coils at a suitable distance from each other, the data transmission interface initiates communication between the stationary and mobile electronics. The parameters related to the charging process are exchanged and the system enters the charging mode. Moving the coils away from each other (MOBOT® driving away) breaks communication, and the charging process stops automatically. Thus, even a short stoppage of the MOBOT® allows you to recharge the battery.
Despite more than 5 times shorter operating time of the MW FlatRunner with lithium batteries compared to the MW FlatRunner with lead-acid batteries, the induction system allows the system to run continuously. This is due to the fact that there is no need to disconnect the MOBOT® from work for the time of replacing the cassettes or stopping the MOBOT® during charging directly using the connector available on the truck.
Table 1. Inductive charging system parameters for MOBOT® AGV FlatRunner MW
Electrical parameters | ||
Input voltage | 1 x 230 V AC ± 10%, 50 Hz | |
Rated voltage | 48 V DC | |
Max. output voltage | 60 V DC | |
Min. output voltage | 15 V DC | |
Max. output power | 3 kW | |
Max. output current | 60 A DC | |
Loading time | ~ 45 min | |
Working time | ~ 1.5 h 1 | |
Mechanical parameters | ||
Distance between stationary coil and coil mobile | Nominal distance: 18 mm | |
Humidity | <95%, non-condensing | |
Working temperature | Charger Stationary coil Mobile coil Cart Mount Electronics | - 10… + 40 ° C - 10… + 40 ° C - 10… + 40 ° C - 10… + 60 ° C |
Storage temperature | - 20… + 55 ° C | |
Noise | 55 dB (A) | |
Charger dimensions | 385x309x127 mm (height x width x depth) | |
Stationary coil dimensions | 360 x 150 x 20 mm (L x W x D) | |
Stationary coil cord length | 3 m | |
What if I don't want to interfere with the floor?
A common problem we encounter with customers, such as a manufacturer of truck-mounted trucks without an operator, is prohibition of any interference with the floor. This is mainly due to the rental of usable areas, local health and safety regulations or the use of high-storage forklifts, for which slight unevenness may be dangerous. We've had a solution for navigation for a long time. Instead of coding or color tapes, we use LMS (Laser Mapping System).
Now we also have a boot system solution. To avoid the need to make a groove for the cables supplying the stationary coil, placed on the floor, WObit can provide a mat in which the coil will be built and the cables will be hidden, and the MOBOT® can easily handle entering and exiting the coil.
1 The actual operating time of the truck without an operator depends, among other things. the working conditions of the trolley, in particular the load carried, the speed of the trolley or the ground on which it is moving.